| CAS
NO. |
58001-44-8
(Base)
61177-45-5 (Potassium) |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
261-069-2,
262-640-9 |
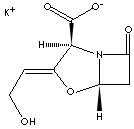
| FORMULA |
C8H8NO5·K |
| MOL
WT. |
237.24 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
Clavulanic Acid
Potassium; |
| Potassium
[2R-(2a,3Z,5a)]-3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7 -oxo-4-oxa-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylate;
Clavulaninsäure Kalium; ácido clavulanico
de potasio; Acide clavulanique potassium; |
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white
to off-white powder |
| MELTING
POINT |
|
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| NFPA
RATINGS |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
| beta-Lactamase
inhibitor to increase antibiotic effectiveness;
used in combination with penicillins (mainly amoxicillin)
to treat infections caused by beta-lactamase–producing organisms.
Beta-lactamase enzymes are produced by some bacteria and have resistance ability
to beta-lactam antibiotics. These enzymes deactivate the antibacterial
properties of beta-lactam antibiotics by opening the beta-lactam ring.
Beta-lactamase inhibitors have little antimicrobial functions themselves and are
combined with an actual beta-lactam antibiotic. Beta-lactamase inhibitors'
function is to bind beta-lactamase enzymes to form an inactive molecule so that
the actual beta-lactam antibiotic access to the bacterial wall which it
destroys. Beta-lactamase inhibitors include clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and
tazobactam. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION (USP, BP) |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white
to off-white powder |
|
BLEND
|
Potassium clavulanate--silicon dioxide (1:1) |
|
CONTENT
|
38.5
- 44.5% (Clavulanic acid)
|
|
WATER
|
1.5%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in fiber drum
|
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
SHELF-LIFE:
3 years
PRICE
INFORMATION
 |
